42 chapter 2 matter and change worksheet answers
If self-employed, first complete Worksheet 2-3 to figure your expected deduction for self-employment tax. Subtract the amount from Worksheet 2-3, line 11, to figure the line 1 entry: 1. 2. If you: • Don’t plan to itemize deductions on Schedule A (Form 1040), use Worksheet 2-4 to figure your expected standard deduction. What is the difference between a heterogeneous and a homogeneous mixture? Homogeneous mixtures have the same composition throughout (such as ketchup), whereas ...5 pages
“Matter and Change”. 2. Section 2.1. Properties of Matter. OBJECTIVES: ... Matter is anything that: a) has mass, and b) takes up space; Mass = a measure of ...
Chapter 2 matter and change worksheet answers
When antimatter encounters ordinary matter, both are annihilated and their mass is converted into energy in the form of gamma rays (γ)—and other much smaller subnuclear particles, which are beyond the scope of this chapter—according to the mass-energy equivalence equation E = mc 2, seen in the preceding section. For example, when a ... 2. Identify what physical change occurs during the following separation processes. a) Distillation of a solution comprising of 50:50 acetone and water b) Filtration to remove tea leaves from tea. c) Evaporation for water from a sugar solution to obtain sugar crystals. Software for math teachers that creates custom worksheets in a matter of minutes. Try for free. Available for Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, Precalculus, and Calculus.
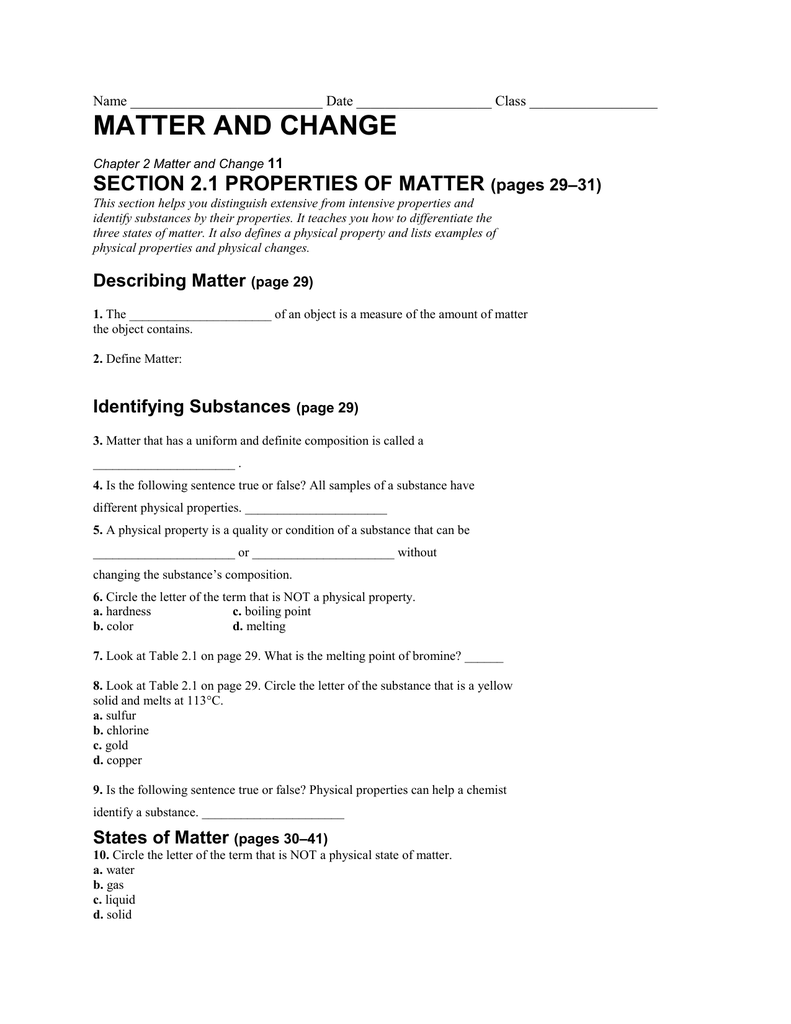
Chapter 2 matter and change worksheet answers. Answers for Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises. 2. Liquids can change their shape (flow); solids can’t. Gases can undergo large volume changes as pressure changes; liquids do not. Gases flow and change volume; solids do not. 4. The mixture can have a variety of compositions; a pure substance has a definite composition. To determine equilibrium warming in 2030 due to continued emissions of CO 2 at the 1990 level, find the point on the curve labeled "CO 2" that is vertically above 0 percent change on the bottom scale. The equilibrium warming on the right-hand scales is about 0.23°C (0.4°F) for a climate system with 1° sensitivity and about 1.2°C (2.2°F ... MATTER AND CHANGE 2 SECTION 2.1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER (pages 39–42) This section helps you ... 12 Guided Reading and Study Workbook 05_Chem_GRSW_Ch02. MATTER AND CHANGE. PET. HELIOLI. II. I IIIIIIIIIIIII. Practice Problems. In your notebook, solve the following problems. SECTION 2.1 PROPERTIES OF MATTER.6 pages
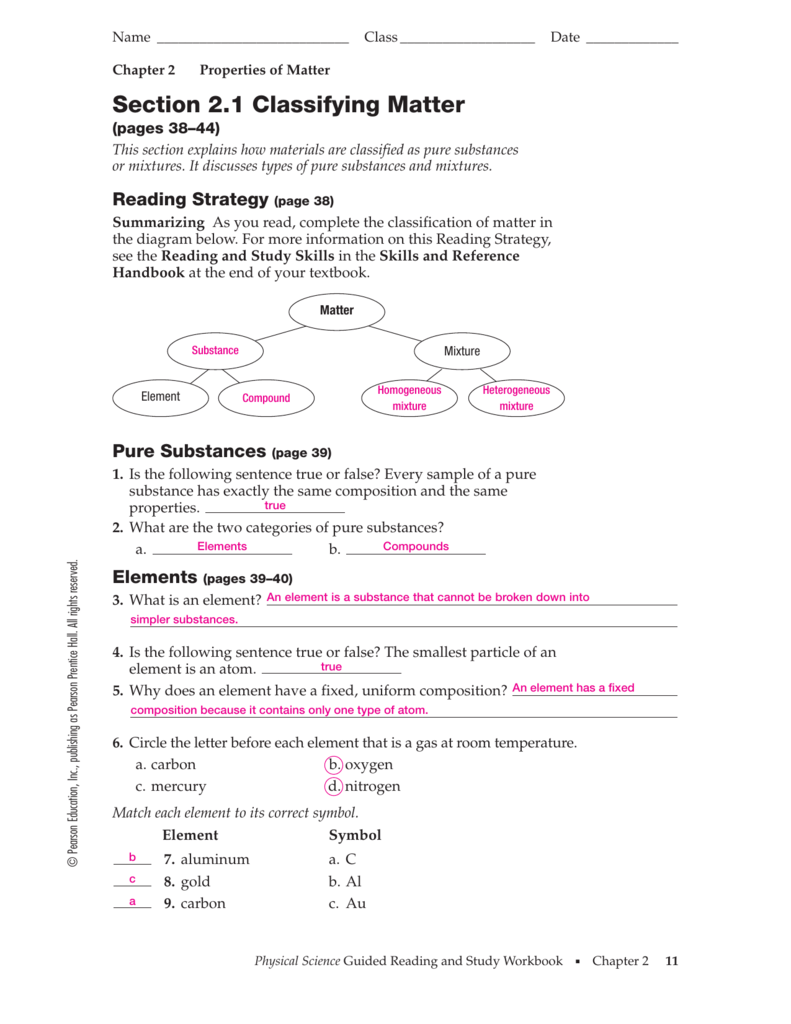
Chapter 2. Matter and Change. Chemistry pg. 38. 2.1 Properties of Matter. Properties used to describe matter are classified as:. 1) Solid- matter that can not flow (definite shape) and has definite volume. 2) Liquid- definite volume but takes the shape of its container (flows). 3) Gas- a ...31 pages Chapter 2 Matter and Change 11 ... 12 Guided Reading and Study Workbook ... This section explains a key difference between an element and a compound, and.8 pages See Chapter 2 of this document for more discussion on genetic variation and natural selection, and pages 158 and 185 of the National Science Education Standards. 9. Evolution: Inquiries into Biology and Earth Science by BSCS. 1992. Seattle: Videodiscovery, pp. 49-53 and pp. 211-221. 10. Standards, p. 117. 11. Earth Science Curriculum Project ...
2.1 Properties of Matter 2.2 Mixtures 2.3 Elements and Compounds 2.4 Chemical Reactions Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Rating: 5 · 1 review Software for math teachers that creates custom worksheets in a matter of minutes. Try for free. Available for Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, Geometry, Algebra 2, Precalculus, and Calculus. 2. Identify what physical change occurs during the following separation processes. a) Distillation of a solution comprising of 50:50 acetone and water b) Filtration to remove tea leaves from tea. c) Evaporation for water from a sugar solution to obtain sugar crystals. When antimatter encounters ordinary matter, both are annihilated and their mass is converted into energy in the form of gamma rays (γ)—and other much smaller subnuclear particles, which are beyond the scope of this chapter—according to the mass-energy equivalence equation E = mc 2, seen in the preceding section. For example, when a ...




















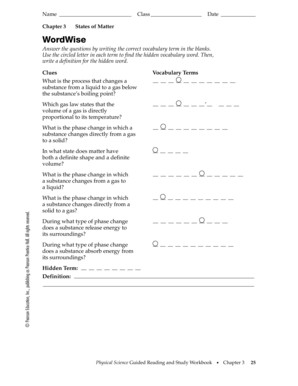









0 Response to "42 chapter 2 matter and change worksheet answers"
Post a Comment